
Soluble guanylate cyclase and NO/cGMP signalling in vascular disease

NO-independent stimulators and activators of soluble guanylate cyclase:

Cellular cyclic GMP is increased by activation of soluble guanylate cyclase
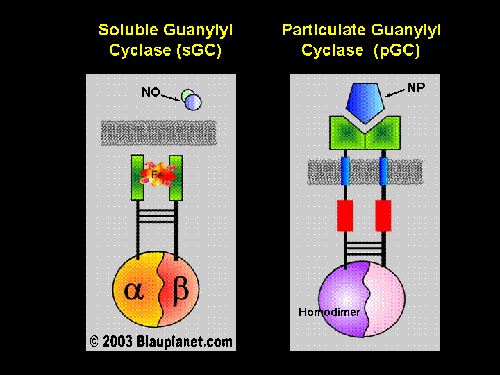
Soluble and Particulate Guanylyl Cyclase

The heterodimeric soluble guanylyl cyclase consists of a heme domain,

Marletta Lab - Soluble Guanylate Cyclase
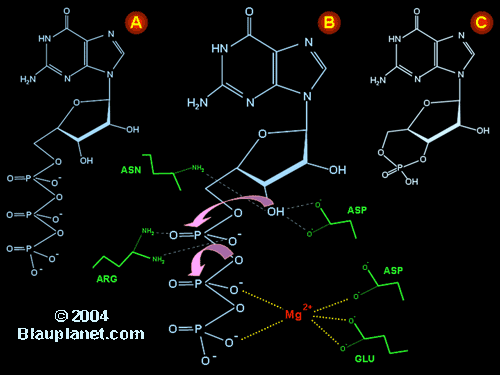
Catalysis of cyclic GMP synthesis by soluble guanylyl cyclase.

Figure 1: Schematic presentation of the soluble guanylate cyclase screening

Soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) catalyzes the conversion of GTP to the

Soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC) is a cytosolic signaling enzyme closely
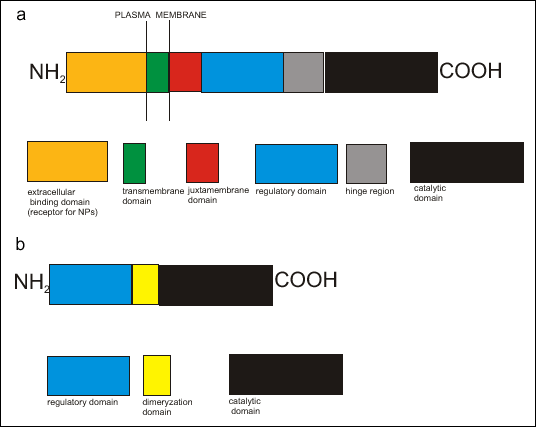
b) soluble guanylate cyclase

of the NO binding heme domain of the soluble guanylyl cyclase receptor.

NO-independent stimulators and activators of soluble guanylate cyclase:

GTP (Guanosine 5`-triphosphate), sGC (Soluble guanylate cyclase).

Tonic and acute nitric oxide signaling through soluble guanylate cyclase is

GTP (Guanosine 5`-triphosphate), sGC (Soluble guanylate cyclase).

Inhibition of soluble guanylate cyclase prevents the AQP1 conductance response to SNP

Revisiting the kinetics of nitric oxide (NO) binding to soluble guanylate

nuclear factor-κB; NO, nitric oxide; sGC, soluble guanylate cyclase.

Effect of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase-Specific Inhibitor on Tissue Relaxation
No comments:
Post a Comment